对称加密:加密和解密使用相同的密钥。
非对称加密:加密和解密采用不同的密钥。数字签名中的公钥和私钥就是两种不同的密钥。
摘要算法:把任意长度的输入数据计算输出固定长度的数据,相同数据计算输出相同的结果,不同数据计算后尽量输出不同的结果。
对称加密:
1、AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), 是DES算法的替代者。
AES支持三种长度的密钥(128位,192位,256位)
AES加密步骤:
1、把明文按照128bit大小拆分成若干个明文块,最后一个明文块补足128bit.
2、将每一个明文块按加密器和密钥分别加密成密文块
3、拼接所有的密文块,成为最终的密文结果。
说明1: AES使用分组加密特性,在对明文加密时,并不是把整段明文一次加密成一段密文,而是把明文拆分成一个个独立的明文块(128bit),每个明文块经过AES加密码后生成一个个独立的密文民块,把这些密文块拼接在一起,就是最终的AES加密结果。若明文不能被128整除,则最后一个明文块需要填充补足到128bit.
补足到128bit有如下几种方式:
- NoPadding 不做任何填充,但要求明文必须是16字段的整数倍。
- PKCS5Padding(默认)如果明文块少于16个字节(128bit),在明文块未尾补足相应数量的字符,且每个字节的值等于缺少的字符数。
- ISO10126Padding: 如果明文块少于16个字节(128bit),在明文块未尾补足相应数量的字节,最后一个字符值等于缺少的字符数,其他字符填充随机数
说明2: AES提供了五种不同的把明文块加密成密文块的工作模式,在加密时使用了一种加密模式,在解密时必须也使用相同模式解密。
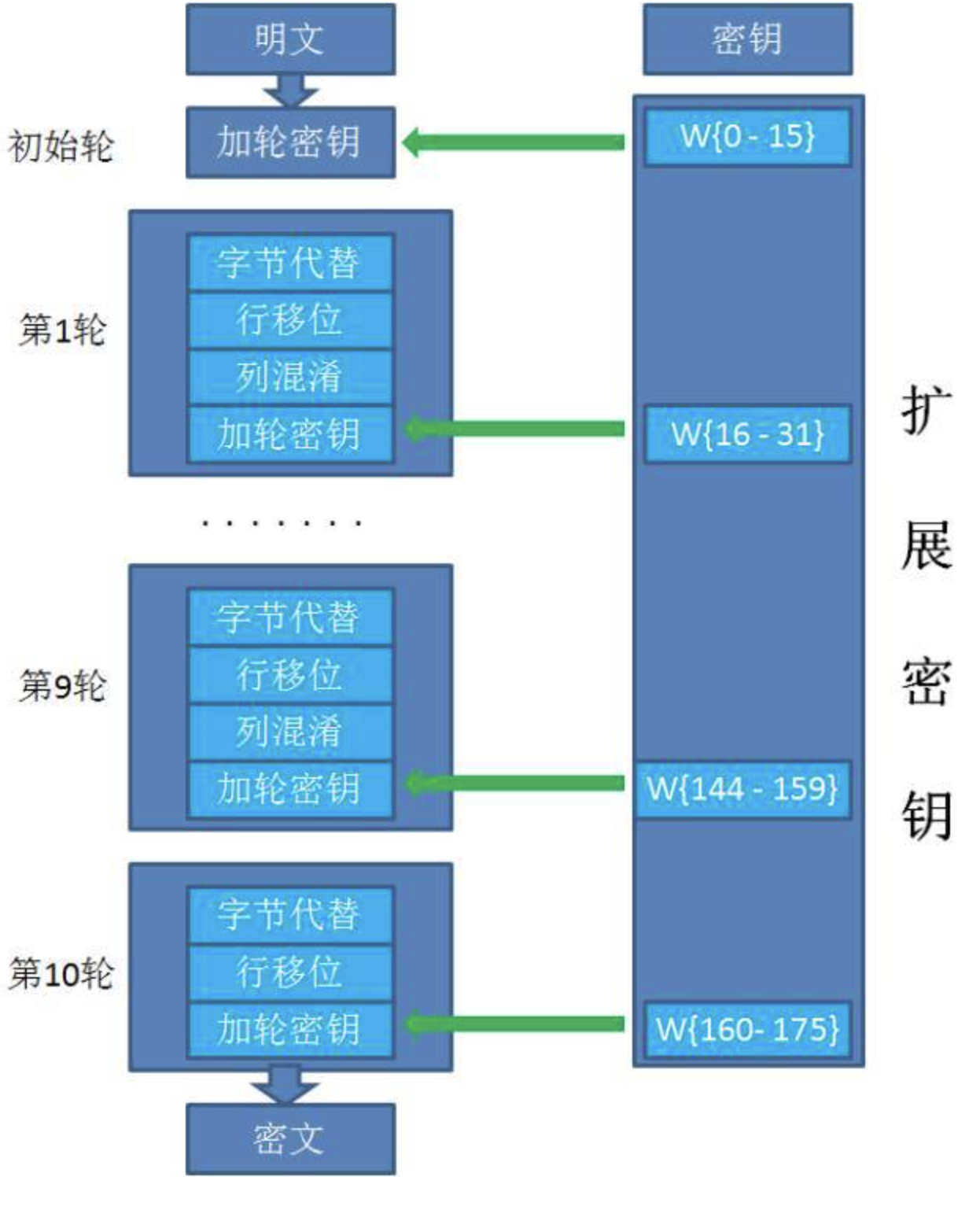
具体多少轮,根据密钥长度确定:
AES128: 10轮;AES192: 12轮;AES256: 14轮
说明3:AES加密算法提供了5种不同的工作模式:ECB CBC CTR CFB OFB
ECB:Electronic Codebook Book, 最简单的工作模式,在该模式下,每一个明文块的加密是独立的,互不干扰。
CBC: Cipher Block Chaining , 可以将相同的明文段加密成不同的密文段。
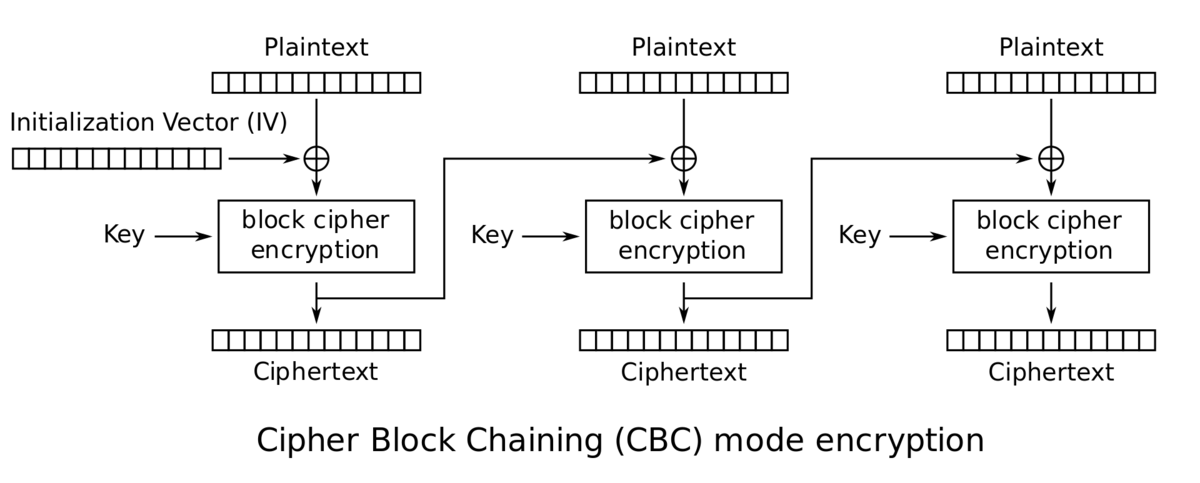
CBC在加密里,需要使用IV,为一个8位字符,初始化IV只有在第一块加密时才会使用,而第N场的加密IV则是用的N-1(N>1)个加密后的二进制数组。上图中+号为异或操作。
AES解密使用反向操作得到原始明文。
import javax.crypto.*; import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec; import java.security.InvalidKeyException; import java.security.Key; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; import java.security.SecureRandom; import java.util.Base64; public class AESTest { public static final String password = "1"; public static void main(String[] args) { String source = "Hello world....."; Key key = createKey(password); byte[] encryptCode = jdkAES(source, key); decrypt(encryptCode, key); } public static Key createKey(String password){ try{ KeyGenerator keyGenerator; keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES"); keyGenerator.init(128, new SecureRandom(password.getBytes())); SecretKey secretKey = keyGenerator.generateKey(); byte[] keyBytes = secretKey.getEncoded(); Key key = new SecretKeySpec(keyBytes, "AES"); return key; } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e){ e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } public static byte[] jdkAES(String context, Key key){ try{ //加密/解密算法-工作模式-填充模式 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5PAdding"); cipher.init(cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key); byte[] result = cipher.doFinal(context.getBytes()); System.out.println("jdk aes:" + new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode(result))); return result; }catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException | NoSuchPaddingException | InvalidKeyException | IllegalBlockSizeException | BadPaddingException e){ e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } public static void decrypt(byte[] result , Key key){ Cipher cipher; try{ cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding"); cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key); result = cipher.doFinal(result); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InvalidKeyException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (NoSuchPaddingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (BadPaddingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("jdk aes descrypt:" + new String(result)); } }
2、DES(Data Encryption Standard),数据加密标准。
DES使用64位分组长度和56位密钥长度,将64位输入转换为64位密文输出,加密与解密使用相同中的步骤和密钥。
密钥长度为64位,但只有56位参与DES运算(第8/16/24/32/40/48/56/65是校验位,分组后的明文组与56位密钥按位替代或交换的方式形成密文组。
** DES使用56位密钥,以现代计算能力,24小时内即可被破解
import javax.crypto.Cipher; import javax.crypto.SecretKeyFactory; import javax.crypto.spec.DESKeySpec; import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.security.InvalidKeyException; import java.security.Key; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; import java.security.spec.InvalidKeySpecException; import java.util.Base64; public class DESTest { //偏移变量,固定占8位字节 //若为CBC分隔模式,则可添加IV,作用相当于salt, public static final String IV_PARAMETER = "12345678"; private static final String CHARSET = "utf-8"; public static Key generateKey(String password) throws InvalidKeyException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeySpecException, UnsupportedEncodingException { DESKeySpec keySpec = new DESKeySpec(password.getBytes(CHARSET)); //加密/解密算法-工作模式-填充模式 //默认使用ECB的分隔方式 SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DES"); return keyFactory.generateSecret(keySpec); } public static String encrypt(String password, String data) { try { Key secretKey = generateKey(password); Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding"); IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(IV_PARAMETER.getBytes(CHARSET)); cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey); byte[] bytes = cipher.doFinal(data.getBytes(CHARSET)); return new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode(bytes)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } public static String decrypt(String password, String encrytedStr){ try { Key secretKey = generateKey(password); Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding"); IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(IV_PARAMETER.getBytes(CHARSET)); cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey, iv); return new String(cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encrytedStr.getBytes(CHARSET))), CHARSET); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } public static void main(String[] args) { // * 此处密钥只使用前8位字节,若不足8位,则为抛出(InvalidKeyException: Wrong key size) 异常 String password = "1aaabbbcccfewfewfew"; String source = "hello world..."; String encrypt = encrypt(password, source); System.out.println(encrypt); System.out.println(decrypt(password, encrypt)); } }
3、3DES(Triple DES) 是DES向AES过渡的加密算法,将DES重复3次形成密文。
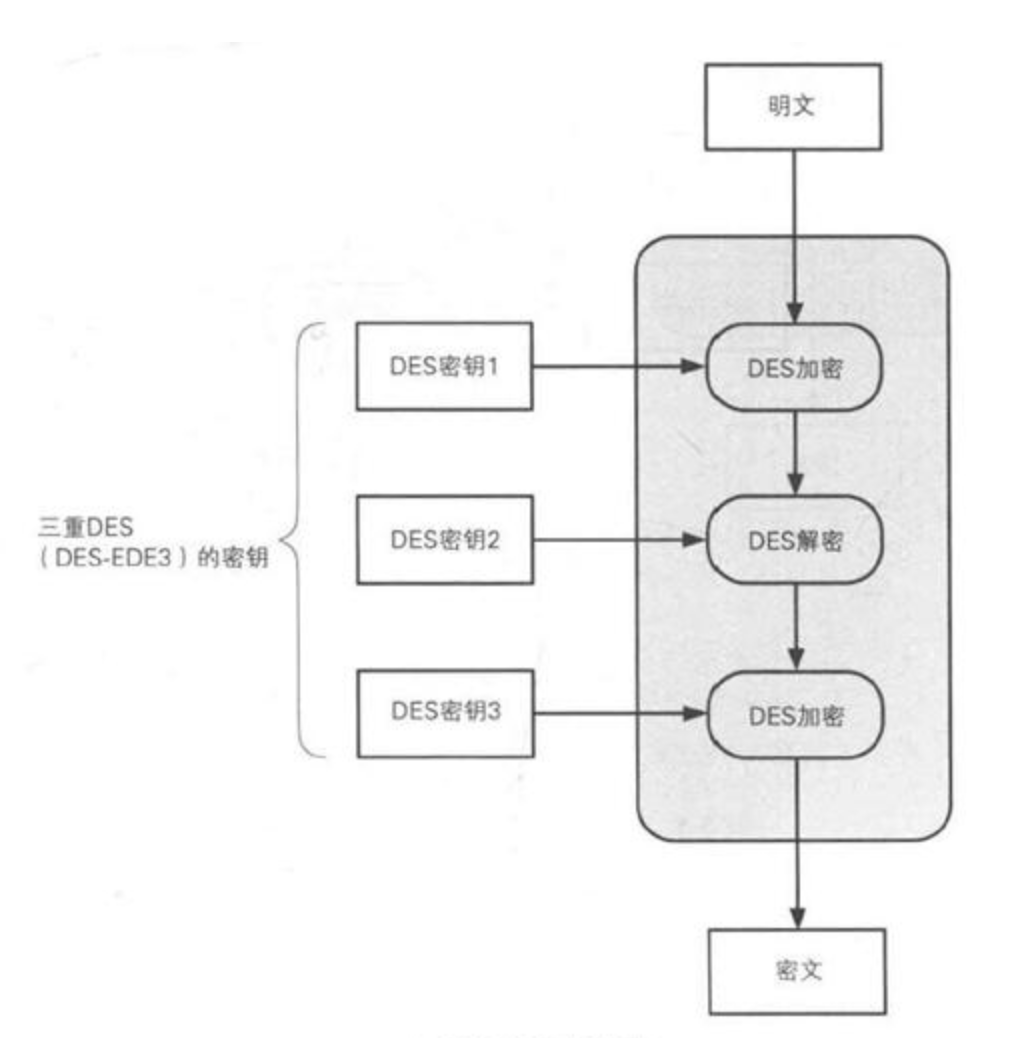
3DES的密钥长度为(56*3=168或112)位,在加密过程中有解密,若3次密钥相同,则转变成了普通DES。
3DES密钥长度较长,安全性较高。
import javax.crypto.Cipher; import javax.crypto.SecretKeyFactory; import javax.crypto.spec.DESedeKeySpec; import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.security.InvalidKeyException; import java.security.Key; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; import java.security.spec.InvalidKeySpecException; import java.util.Base64; /** * 3DES Test */ public class DESedeTest { //偏移变量,固定占8位字节 public static final String IV_PARAMETER = "12345678"; private static final String CHARSET = "utf-8"; public static Key generateKey(String password) throws InvalidKeyException, NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeySpecException, UnsupportedEncodingException { DESedeKeySpec keySpec = new DESedeKeySpec(password.getBytes(CHARSET)); //加密/解密算法-工作模式-填充模式 //默认使用ECB的方式 SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DESede"); return keyFactory.generateSecret(keySpec); } public static String encrypt(String password, String data) { try { Key secretKey = generateKey(password); Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DESede/CBC/PKCS5Padding"); IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(IV_PARAMETER.getBytes(CHARSET)); cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey, iv); // 可以不使用iv cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey, iv); byte[] bytes = cipher.doFinal(data.getBytes(CHARSET)); return new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode(bytes)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } public static String decrypt(String password, String encrytedStr){ try { Key secretKey = generateKey(password); Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DESede/CBC/PKCS5Padding"); IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(IV_PARAMETER.getBytes(CHARSET)); cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey, iv); return new String(cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encrytedStr.getBytes(CHARSET))), CHARSET); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } public static void main(String[] args) { // * 此处密钥只使用前24位字节,若不足24位,则为抛出(InvalidKeyException: Wrong key size) 异常 String password = "123456789012345678901234"; String source = "hello world..."; String encrypt = encrypt(password, source); System.out.println(encrypt); System.out.println(decrypt(password, encrypt)); } }
非对称加密:
非对称加密需要两个密钥:公钥(publickey)和私钥(privatekey)。公钥加密,私钥解密;私钥加密,公钥解密。
1、RSA
RSA是目前使用最广泛的公钥密码体制之一。RSA密码体制既可以用于加密又可以用于数字签名。其它全性是基于极其困难的大整数分解(两个素数的乘积)
在使用时生成一对RSA密钥,由用户保存私钥,公钥可以对外公开。为了提高保密强度,RSA密钥至少为500位长,一般推荐1024位。
由于加解密速度慢,一般使用对称加密算法与RSA结合使用,报文使用DES或AES加密,密钥通过RSA加密后一起传输。
import javax.crypto.*; import java.security.*; import java.security.interfaces.RSAPrivateKey; import java.security.spec.PKCS8EncodedKeySpec; import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec; import java.util.Base64; public class RSATest { private static String publicKeyStr = ""; private static String privateKeyStr = ""; public static void generateKey() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA"); keyPairGenerator.initialize(1024, new SecureRandom()); KeyPair keyPair = keyPairGenerator.generateKeyPair(); PrivateKey privateKey = (RSAPrivateKey) keyPair.getPrivate(); PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic(); publicKeyStr = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(publicKey.getEncoded()); privateKeyStr = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(privateKey.getEncoded()); // System.out.println(publicKeyStr); // System.out.println(privateKeyStr); } public static String encrypt(String str, String publicKeyStr) throws Exception { byte[] decoded = Base64.getDecoder().decode(publicKeyStr); PublicKey publicKey = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA").generatePublic(new X509EncodedKeySpec(decoded)); Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA"); cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKey); String outStr = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(cipher.doFinal(str.getBytes())); return outStr; } public static String decrypt(String str, String privateKeyStr) throws Exception{ byte[] inputByte = Base64.getDecoder().decode(str.getBytes()); byte[] decoded = Base64.getDecoder().decode(privateKeyStr); PrivateKey privateKey = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA").generatePrivate(new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(decoded)); Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA"); cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKey); String outStr = new String(cipher.doFinal(inputByte)); return outStr; } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { generateKey(); String message = "12345678"; System.out.println("source:" + message); String messageEncrypt = encrypt(message, publicKeyStr); System.out.println("encrypted:" + messageEncrypt); String messageDecrypt = decrypt(messageEncrypt, privateKeyStr); System.out.println("decrypted:" + messageDecrypt); } }
2、DSA
DSA一般用于数字签名和认证,基于整数有限域离散对数难题的,其安全性与RSA相比差不多
DSA做签名时速度更快,但做签名验证时速度较慢,一般情况验证签名的次数多于签名的次数。
摘要算法:
1、MD5(Message Digest Algorithm)
MD5是一种哈希算法,输入作意长度的信息,经过处理,输出为128位的信息,不同的输入得到不同的输出结果。
import java.math.BigInteger; import java.security.MessageDigest; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; public class MD5Test { public static byte[] toMD5(byte[] input){ MessageDigest md = null; try{ md = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5"); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } md.update(input); return md.digest(); } public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "123456"; byte[] r = toMD5(str.getBytes()); //MD5返回16个byte(java基本类型) 每个byte占8位,共128位 //以16进制的方式转换为字符串 System.out.println(new BigInteger(1, r).toString(16)); String salt = "random"; byte[] saltDigest = toMD5((str + salt).getBytes()); System.out.println(new BigInteger(1, saltDigest).toString(16)); } }
2、SHA-1(Secure Hash Algorithm)
SHA-1主要适用于签名标准(DSS)里定义的数字签名算法。对于输入信息,输出为160bit的数据。 它同类型算法有SHA-256和SHA-512.
SHA-1在Java中的实现与MD5类似。
国密算法:
国密即国家密码局认定的国产密码算法。主要有SM1,SM2,SM3,SM4。密钥长度和分组长度均为128位。
- SM1 为对称加密。其加密强度与AES相当。该算法不公开,调用该算法时,需要通过加密芯片的接口进行调用。
- 采用该算法已经研制了系列芯片、智能IC卡、智能密码钥匙、加密卡、加密机等安全产品,广泛应用于电子政务、电子商务及国民经济的各个应用领域(包括国家政务通、警务通等重要领域)。
- SM2为非对称加密,基于ECC。该算法已公开。由于该算法基于ECC,故其签名速度与秘钥生成速度都快于RSA。ECC 256位(SM2采用的就是ECC 256位的一种)安全强度比RSA 2048位高,但运算速度快于RSA。
- SM3 消息摘要。可以用MD5作为对比理解。该算法已公开。校验结果为256位。
- SM4 无线局域网标准的分组数据算法。对称加密,密钥长度和分组长度均为128位。
由于SM1、SM4加解密的分组大小为128bit,故对消息进行加解密时,若消息长度过长,需要进行分组,要消息长度不足,则要进行填充
reference: