–老年菜鸡的基础数论之旅
A – Bi-shoe and Phi-shoe
Description
给定一个序列,序列每个值x有一个花费,x的花费为一个欧拉函数值大于等于x的数y,求最小花费
Solution
首先我们要使求得花费最小,那就找一个刚好满足欧拉函数值大于等于x的数嘛,然后我们知道素数p的欧拉函数值为p-1,所以我们可以从x+1开始找,就减少了查找区间,降低了复杂度


1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 3 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 4 using namespace std; 5 using ll = long long; 6 using ull = unsigned long long; 7 using pa = pair<int, int>; 8 using ld = long double; 9 const int maxn = 1e6 + 1e5; 10 int n, m, k; 11 int p[maxn], e[maxn]; 12 void init() 13 { 14 for (int i = 2; i < maxn; i++) 15 e[i] = i; 16 for (int i = 2; i < maxn; ++i) 17 { 18 if (e[i] == i) 19 { 20 for (int j = i; j < maxn; j += i) 21 e[j] = e[j] / i * (i - 1); 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 26 { 27 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 28 cin.tie(0); 29 cout.tie(0); 30 init(); 31 int t; 32 cin >> t; 33 int c = 1; 34 while (t--) 35 { 36 ll ans = 0; 37 cin >> n; 38 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 39 { 40 int x; 41 cin >> x; 42 for (int j = x + 1; j < maxn; j++) 43 if (e[j] >= x) 44 { 45 ans += j; 46 break; 47 } 48 } 49 cout << "Case " << c << ": " << ans << " Xukha "; 50 ++c; 51 } 52 return 0; 53 }
View Code
B – Prime Independence
Description
给定一个序列,要求求出序列中的最大分配集,一个分配集里的数不能出现两两相除商不是素数的情况
Solution


1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 3 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 4 using namespace std; 5 using ll = long long; 6 using ull = unsigned long long; 7 using pa = pair<int, int>; 8 using ld = long double; 9 int n, m, k; 10 const int maxE = 5e5 + 10; 11 const int maxn = 4e4 + 10; 12 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 13 vector<int> G[maxn]; 14 int uN; 15 int Mx[maxn], My[maxn]; 16 int dx[maxn], dy[maxn]; 17 int dis; 18 bool used[maxn]; 19 bool SearchP() 20 { 21 queue<int> Q; 22 dis = INF; 23 memset(dx, -1, sizeof(dx)); 24 memset(dy, -1, sizeof(dy)); 25 for (int i = 1; i <= uN; i++) 26 if (Mx[i] == -1) 27 { 28 Q.push(i); 29 dx[i] = 0; 30 } 31 while (!Q.empty()) 32 { 33 int u = Q.front(); 34 Q.pop(); 35 if (dx[u] > dis) 36 break; 37 int sz = G[u].size(); 38 for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) 39 { 40 int v = G[u][i]; 41 if (dy[v] == -1) 42 { 43 dy[v] = dx[u] + 1; 44 if (My[v] == -1) 45 dis = dy[v]; 46 else 47 { 48 dx[My[v]] = dy[v] + 1; 49 Q.push(My[v]); 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 return dis != INF; 55 } 56 bool DFS(int u) 57 { 58 int sz = G[u].size(); 59 for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) 60 { 61 int v = G[u][i]; 62 if (!used[v] && dy[v] == dx[u] + 1) 63 { 64 used[v] = true; 65 if (My[v] != -1 && dy[v] == dis) 66 continue; 67 if (My[v] == -1 || DFS(My[v])) 68 { 69 My[v] = u; 70 Mx[u] = v; 71 return true; 72 } 73 } 74 } 75 return false; 76 } 77 int MaxMatch() 78 { 79 int res = 0; 80 memset(Mx, -1, sizeof(Mx)); 81 memset(My, -1, sizeof(My)); 82 while (SearchP()) 83 { 84 memset(used, false, sizeof(used)); 85 for (int i = 1; i <= uN; i++) 86 if (Mx[i] == -1 && DFS(i)) 87 res++; 88 } 89 return res; 90 } 91 92 template <class T> 93 inline void read(T &ret) 94 { 95 int f = 1; 96 ret = 0; 97 char ch = getchar(); 98 while (!isdigit(ch)) 99 { 100 if (ch == '-') 101 f = -1; 102 ch = getchar(); 103 } 104 while (isdigit(ch)) 105 { 106 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 107 ch = getchar(); 108 } 109 ret *= f; 110 } 111 template <class T> 112 inline void write(T n) 113 { 114 if (n < 0) 115 { 116 putchar('-'); 117 n = -n; 118 } 119 if (n >= 10) 120 { 121 write(n / 10); 122 } 123 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 124 } 125 int a[maxn]; 126 int xx, tot = 1; 127 unordered_map<int, int> pos; 128 int prime[maxE]; 129 int notp[maxE]; 130 int pcnt; 131 inline void init() 132 { 133 for (int i = 2; i < maxE; i++) 134 { 135 if (!notp[i]) 136 { 137 prime[pcnt++] = i; 138 for (int j = 0; j < pcnt && i * prime[j] < maxE; j++) 139 { 140 notp[i * prime[j]] = 1; 141 if (i % prime[j] == 0) 142 break; 143 } 144 } 145 } 146 } 147 inline void add(int x, int id) 148 { 149 int fac[maxn / 10]; 150 int tot = 0; 151 for (int i = 0; prime[i] * prime[i] <= x; i++) 152 { 153 if (x % prime[i] == 0) 154 { 155 fac[tot++] = prime[i]; 156 while (x % prime[i] == 0) 157 x /= prime[i]; 158 } 159 } 160 if (x > 1) 161 fac[tot++] = x; 162 x = a[id]; 163 for (int i = 0; i < tot; i++) 164 { 165 int cur = x / fac[i]; 166 if (pos[cur]) 167 { 168 G[id].emplace_back(pos[cur]); 169 G[pos[cur]].emplace_back(id); 170 } 171 } 172 } 173 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 174 { 175 init(); 176 int t; 177 // scanf("%d", &t); 178 read(t); 179 while (t--) 180 { 181 read(n); 182 // scanf("%d", &n); 183 pos.clear(); 184 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 185 { 186 read(a[i]); 187 // scanf("%d", &a[i]); 188 pos[a[i]] = i; 189 G[i].clear(); 190 } 191 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 192 { 193 add(a[i], i); 194 } 195 uN = n; 196 printf("Case %d: %d ", tot++, n - MaxMatch() / 2); 197 } 198 return 0; 199 }
View Code
C – Aladdin and the Flying Carpet
Description
每次查询给出两个数n,a,求出所有的满足(i<j,i*j=n,且min(i,j)>=a)的数对个数
Solution
由唯一分解定理可以知道一个正整数n可以唯一分解为n=(p1^r1)*(p2^r2…),其所有约数个数为q=(1+r1)*(1+r2)…,那么约数个数q/2就是所有满足i*j=n的个数,注意到题上说是长方形而非正方形,可以不用考虑完全平方数+1的情况,
然后需要min(i,j)>=b,我们把小于b的约数剪掉即是答案


1 //唯一分解定理 2 //我们知道对于一个正整数n可以分解为n=(p0^a0)*(p1^a1)*...,p为素因子 3 //这时正整数n的约数个数就是(1+a0)*(1+a1)*(1+a2)*(1+a3)... 4 //对于此题,我们可以先用欧拉筛筛出前sqrt(max(a))的数,然后求出约数个数, 5 //约数个数/2即为全部的整数对(i,j)满足i*j=a 6 //要使min(i,j)>=b 7 //我们只需要将前b个自然数中的约数个数剪掉即可 8 //长方形而非正方形,不用考虑完全平方数加1的情况 9 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 10 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 11 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 12 using namespace std; 13 using ll = long long; 14 using ull = unsigned long long; 15 using pa = pair<int, int>; 16 using ld = long double; 17 ll n, m, k; 18 const int maxn = 1e6 + 10; 19 const int mod = 998244353; 20 template <class T> 21 inline T read(T &ret) 22 { 23 int f = 1; 24 ret = 0; 25 char ch = getchar(); 26 while (!isdigit(ch)) 27 { 28 if (ch == '-') 29 f = -1; 30 ch = getchar(); 31 } 32 while (isdigit(ch)) 33 { 34 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 35 ch = getchar(); 36 } 37 ret *= f; 38 return ret; 39 } 40 template <class T> 41 inline void write(T n) 42 { 43 if (n < 0) 44 { 45 putchar('-'); 46 n = -n; 47 } 48 if (n >= 10) 49 { 50 write(n / 10); 51 } 52 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 53 } 54 ll prime[maxn]; 55 int vis[maxn]; 56 int cnt = 0; 57 void init() //欧拉筛 58 { 59 for (int i = 2; i < maxn; i++) 60 { 61 if (!vis[i]) 62 prime[cnt++] = i; 63 for (int j = 0; j < cnt && prime[j] * i < maxn; j++) 64 { 65 vis[prime[j] * i] = 1; 66 if (i % prime[j] == 0) 67 break; 68 } 69 } 70 } 71 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 72 { 73 init(); 74 int t; 75 read(t); 76 int tot = 0; 77 while (t--) 78 { 79 ll a, b; 80 read(a); 81 read(b); 82 int ans = 0; 83 if (b * b <= a) 84 { 85 ll tmp = a; 86 ans = 1; 87 for (int i = 0; i < cnt && prime[i] <= sqrt(tmp); i++) 88 { 89 if (tmp % prime[i] == 0) 90 { 91 int cur = 0; 92 while (tmp % prime[i] == 0) 93 { 94 ++cur; 95 tmp /= prime[i]; 96 } 97 ans *= (1 + cur); 98 } 99 } 100 if (tmp > 1) 101 ans <<= 1; 102 // if (ans & 1) 103 // ++ans; 104 ans >>= 1; 105 for (int i = 1; i < b; i++) 106 if (a % i == 0) 107 --ans; 108 } 109 printf("Case %d: %d ", ++tot, ans); 110 } 111 return 0; 112 }
View Code
D – Sigma Function
Description
给定一个自然数n,求出小于n的自然数有多少个的约数之和为偶数,输出数量
Solution
n=(p1^r1)*(p2^r2…),约数之和a=(1+p1+p1^2+..p1^r1)*(1+p2+p2^2+..p2^2)….,等比求和即可得到原题式子(然而我并不会用这个推出结论,还是打表来的)
打表找规律,发现为约数和为奇数的数字为完全平方数或者2倍完全平方数,减去即可


1 //一个数所有因子和为(1+p1+p1^2+...+p1^e1)*(1+p2+p2^2+...p2^e2)*...() 2 //打表发现因子和为奇数的数是平方数或2倍平方数 3 //减去即可 4 //注意sqrt返回值为浮点数,需要转换为ll,不然double/float转ll会丢失精度,就wa 5 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 6 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 7 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 8 using namespace std; 9 using ll = long long; 10 using ull = unsigned long long; 11 using pa = pair<int, int>; 12 using ld = long double; 13 ll n, m, k; 14 const ll maxn = 1e6; 15 const int mod = 998244353; 16 template <class T> 17 inline T read(T &ret) 18 { 19 int f = 1; 20 ret = 0; 21 char ch = getchar(); 22 while (!isdigit(ch)) 23 { 24 if (ch == '-') 25 f = -1; 26 ch = getchar(); 27 } 28 while (isdigit(ch)) 29 { 30 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 31 ch = getchar(); 32 } 33 ret *= f; 34 return ret; 35 } 36 template <class T> 37 inline void write(T n) 38 { 39 if (n < 0) 40 { 41 putchar('-'); 42 n = -n; 43 } 44 if (n >= 10) 45 { 46 write(n / 10); 47 } 48 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 49 } 50 ll prime[maxn]; 51 int vis[maxn]; 52 int pcnt = 0; 53 void init() //欧拉筛 54 { 55 for (int i = 2; i < maxn; i++) 56 { 57 if (!vis[i]) 58 prime[pcnt++] = i; 59 for (int j = 0; j < pcnt && prime[j] * i < maxn; j++) 60 { 61 vis[prime[j] * i] = 1; 62 if (i % prime[j] == 0) 63 break; 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 ll cal(int p, int n) 68 { 69 ll sum = 1; 70 ll t = 1; 71 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 72 { 73 t *= p; 74 sum += t; 75 } 76 // cout << "sum" 77 // << " :" << p << " " << n << " " << sum << " "; 78 return sum; 79 } 80 int getFacSum(int x) 81 { 82 ll sum = 1; 83 for (int i = 0; i < pcnt && prime[i] * prime[i] <= x; i++) 84 { 85 int p = prime[i]; 86 int cur = 0; 87 while (x % p == 0) 88 { 89 ++cur; 90 x /= p; 91 } 92 ll t = cal(p, cur); 93 sum *= t; 94 } 95 if (x > 1) 96 sum *= cal(x, 1); 97 return sum; 98 } 99 void dabiao() 100 { 101 for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) 102 // getFacSum(i); 103 if (getFacSum(i) & 1) 104 cout << i << ": " << getFacSum(i) << " "; 105 } 106 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 107 { 108 init(); 109 int t; 110 // dabiao(); 111 read(t); 112 int tot = 0; 113 while (t--) 114 { 115 ll x; 116 read(x); 117 ll ans = x; 118 ans = ans - (ll)sqrt(x) - (ll)sqrt(x / 2); 119 printf("Case %d: %lld ", ++tot, ans); 120 } 121 return 0; 122 }
View Code
E – Leading and Trailing
Description
给出一个数以及其幂指数,求出最终结果的前三位和后三位
Solution
对于后三位,直接快速幂即可,高于三位截断
对于前三位其实也阔以这样,不过需要用double(或ld)记录当前答案,不然wa(雾)


1 //低位直接算,大于1000就截掉 2 //高位思想类似,不过需要用double,不然得不到答案(雾) 3 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 4 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 5 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 6 using namespace std; 7 using ll = long long; 8 using ull = unsigned long long; 9 using pa = pair<int, int>; 10 using ld = long double; 11 ll n, m, k; 12 const ll maxn = 1e6; 13 const int mod = 998244353; 14 template <class T> 15 inline T read(T &ret) 16 { 17 int f = 1; 18 ret = 0; 19 char ch = getchar(); 20 while (!isdigit(ch)) 21 { 22 if (ch == '-') 23 f = -1; 24 ch = getchar(); 25 } 26 while (isdigit(ch)) 27 { 28 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 29 ch = getchar(); 30 } 31 ret *= f; 32 return ret; 33 } 34 template <class T> 35 inline void write(T n) 36 { 37 if (n < 0) 38 { 39 putchar('-'); 40 n = -n; 41 } 42 if (n >= 10) 43 { 44 write(n / 10); 45 } 46 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 47 } 48 int qpow2(ll a, int b) 49 { 50 int c = 1000; 51 a %= c; 52 int ans = 1; 53 while (b) 54 { 55 if (b & 1) 56 { 57 ans *= a; 58 if (ans >= c) 59 ans %= c; 60 } 61 a *= a; 62 if (a >= c) 63 a %= c; 64 b >>= 1; 65 } 66 return ans; 67 } 68 int qpow1(ld a, int b) 69 { 70 ll c = 1e4; 71 ld ans = 1; //ll会wa 72 while (b) 73 { 74 if (b & 1) 75 { 76 ans *= a; 77 while (ans >= c) 78 ans /= 10; 79 } 80 a *= a; 81 while (a >= c) 82 a /= 10; 83 b >>= 1; 84 } 85 while (ans >= 1000) 86 { 87 ans /= 10; 88 } 89 return (int)ans; 90 } 91 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 92 { 93 int t; 94 int tot = 0; 95 read(t); 96 while (t--) 97 { 98 ll n; 99 int k; 100 read(n), read(k); 101 ll ff = n; 102 int fa = qpow1(ff, k); 103 ll llt = n; 104 int la = qpow2(llt, k); 105 printf("Case %d: %d %03d ", ++tot, fa, la); 106 } 107 return 0; 108 }
View Code
F – Goldbach`s Conjecture
Description
验证哥德巴赫猜想,给一个大于2的偶数n,找出有多少个素数对a,b满足(a<=b,a+b=n),输出个数
Solution
素数打表到1e7,对于每个查询暴力查询到n/2,记录答案
注意内存限制,需要将标记数组设为short或者bool,prime数组开到1e6即可


1 //素数筛 2 //处理到n/2即可 3 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 4 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 5 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 6 using namespace std; 7 using ll = long long; 8 using ull = unsigned long long; 9 using pa = pair<int, int>; 10 using ld = long double; 11 ll n, m, k; 12 const int maxn = 1e7 + 1000; 13 const int mod = 998244353; 14 template <class T> 15 inline T read(T &ret) 16 { 17 int f = 1; 18 ret = 0; 19 char ch = getchar(); 20 while (!isdigit(ch)) 21 { 22 if (ch == '-') 23 f = -1; 24 ch = getchar(); 25 } 26 while (isdigit(ch)) 27 { 28 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 29 ch = getchar(); 30 } 31 ret *= f; 32 return ret; 33 } 34 template <class T> 35 inline void write(T n) 36 { 37 if (n < 0) 38 { 39 putchar('-'); 40 n = -n; 41 } 42 if (n >= 10) 43 { 44 write(n / 10); 45 } 46 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 47 } 48 int pcnt, prime[maxn / 10]; 49 short vis[maxn]; 50 void init() 51 { 52 vis[0] = vis[1] = 1; 53 for (int i = 2; i < maxn; i++) 54 { 55 if (!vis[i]) 56 prime[pcnt++] = i; 57 for (int j = 0; j < pcnt && prime[j] * i < maxn; j++) 58 { 59 vis[prime[j] * i] = 1; 60 if (i % prime[j] == 0) 61 break; 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 int solve(int n) 66 { 67 int ans = 0; 68 for (int i = 0; i < pcnt && prime[i] <= n / 2; i++) 69 { 70 if (!vis[n - prime[i]]) 71 ++ans; 72 } 73 return ans; 74 } 75 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 76 { 77 init(); 78 int t; 79 scanf("%d", &t); 80 int tot = 0; 81 while (t--) 82 { 83 int n; 84 // read(n); 85 scanf("%d", &n); 86 printf("Case %d: %d ", ++tot, solve(n)); 87 } 88 return 0; 89 }
View Code
G – Harmonic Number (II)
Description
整数分块儿
Solution
对于一个数x,[n/x,n/(n/x)]的值都是n/x,由此暴力即可


1 //整数分块儿 2 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 3 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 4 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 5 using namespace std; 6 using ll = long long; 7 using ull = unsigned long long; 8 using pa = pair<int, int>; 9 using ld = long double; 10 ll n, m, k; 11 const int maxn = 1e7 + 1000; 12 const int mod = 998244353; 13 template <class T> 14 inline T read(T &ret) 15 { 16 int f = 1; 17 ret = 0; 18 char ch = getchar(); 19 while (!isdigit(ch)) 20 { 21 if (ch == '-') 22 f = -1; 23 ch = getchar(); 24 } 25 while (isdigit(ch)) 26 { 27 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 28 ch = getchar(); 29 } 30 ret *= f; 31 return ret; 32 } 33 template <class T> 34 inline void write(T n) 35 { 36 if (n < 0) 37 { 38 putchar('-'); 39 n = -n; 40 } 41 if (n >= 10) 42 { 43 write(n / 10); 44 } 45 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 46 } 47 ll solve(ll n) 48 { 49 ll ans = n + n / 2; 50 for (ll i = 3; i <= n;) 51 { 52 ll to = n / (n / i); 53 ans += (n / i) * (to - i + 1); 54 i = to + 1; 55 } 56 return ans; 57 } 58 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 59 { 60 int t; 61 read(t); 62 int tot = 0; 63 while (t--) 64 { 65 int n; 66 read(n); 67 printf("Case %d: %lld ", ++tot, solve(n)); 68 } 69 return 0; 70 }
View Code
H – Pairs Forming LCM
Description

Solution
由唯一分解定理知,一个数n可以唯一分解为n=(p1r1)*(p2r2…),
假设只有一个质因子p1,指数为r1,则[a,b]=n可以得到a,b的分解必有一个幂次为r1,剩下一个数的幂次可以0,r1任选,一共C(2,1)*(r1+1)种情况,
不过两者都是r1的时候算重叠了,需要减去,则此时对答案的贡献就是2*r1+1,考虑分步原理,每个质因子对答案的贡献都是如此计算,则计算出来ans=(2*r1+1)*(2*r2+1)…
不过由于我们不仅仅计算了,a<b,也计算了a>b,这时候需要将答案除以2,为什么没有考虑a==b呢,因为只有a=b=n这一种情况可以对答案有贡献,最后再加上1即是答案


1 /* 2 唯一分解定理 3 lcm(a,b)=n,则 4 n=p1^r1*p2^r2...pm^rm 5 a=p1^a1*p2^a2...pm^am 6 b=p1^b1*p2^b2...pm^bm 7 对于每一个ri都有ai+bi=ri,且ai,bi必须有一个为ri 8 所以一个ri对应有2(ri+1),(从0开始)种贡献,不过当ai=bi=ri时算了两次,应减去 9 因此最终每一个素因子对答案的贡献就是2*(ri+1)-1=2*ri+1 10 根据分步原理ans=PI(2*ri+1) 11 计算完毕后,我们可以直到,对于所有的a,b我们计算了a>=b和a<b的情况(除了最后a=b=n),即求出的是答案的二倍 12 因此最后答案是ans=ans/2+1 13 */ 14 15 #pragma optmize(3) 16 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 17 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 18 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 19 using namespace std; 20 using ll = long long; 21 using ull = unsigned long long; 22 using pa = pair<int, int>; 23 using ld = long double; 24 ll n, m, k; 25 const int maxn = 1e7 + 1000; 26 const int mod = 998244353; 27 template <class T> 28 inline T read(T &ret) 29 { 30 int f = 1; 31 ret = 0; 32 char ch = getchar(); 33 while (!isdigit(ch)) 34 { 35 if (ch == '-') 36 f = -1; 37 ch = getchar(); 38 } 39 while (isdigit(ch)) 40 { 41 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 42 ch = getchar(); 43 } 44 ret *= f; 45 return ret; 46 } 47 template <class T> 48 inline void write(T n) 49 { 50 if (n < 0) 51 { 52 putchar('-'); 53 n = -n; 54 } 55 if (n >= 10) 56 { 57 write(n / 10); 58 } 59 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 60 } 61 int prime[maxn / 10]; 62 bool vis[maxn]; 63 int pcnt = 0; 64 void init() 65 { 66 vis[0] = vis[1] = 1; 67 for (int i = 2; i < maxn; i++) 68 { 69 if (!vis[i]) 70 prime[pcnt++] = i; 71 for (int j = 0; j < pcnt && i * prime[j] < maxn; j++) 72 { 73 vis[prime[j] * i] = 1; 74 if (i % prime[j] == 0) 75 break; 76 } 77 } 78 } 79 inline ll lcm(ll a, ll b) 80 { 81 ll g = __gcd(a, b); 82 return a / g * b; 83 } 84 ll solve(ll c) 85 { 86 ll ans = 1; 87 for (int i = 0; i < pcnt && prime[i] * prime[i] <= c; i++) 88 { 89 int cur = 0; 90 while (c % prime[i] == 0) 91 { 92 c /= prime[i]; 93 ++cur; 94 } 95 if (cur) 96 ans *= (2 * cur + 1); 97 } 98 if (c > 1) 99 ans *= 3; 100 return ans / 2 + 1; 101 } 102 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 103 { 104 init(); 105 int t; 106 read(t); 107 int tot = 0; 108 while (t--) 109 { 110 ll n; 111 read(n); 112 printf("Case %d: %lld ", ++tot, solve(n)); 113 } 114 return 0; 115 }
View Code
I – Harmonic Number
Description
给定一个整数n,求调和奇数h(n)
Solution
解法1:
记住公式h(n)=ln(n)+C+1/(2n),C为欧拉常数=0.57721566490153286060651209….(仅在数比较大时适用,较小时应采用累加方式计算)
解法2:
打表,可以看出h(n)是有累加性质的,我们每50项记录一个区间答案,即我们记录h(50),h(100),h(150)…
然后对于每个查询都可以在50次运算内找出答案


1 /* 2 h(n)≈ln(n)+C+1/(2*n) 3 C为欧拉常数=0.57721566490153286060651209 4 仅在n比较大时适用 5 6 也阔以打表分50个记录一个 7 */ 8 // #pragma optmize(3) 9 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 10 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 11 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 12 using namespace std; 13 using ll = long long; 14 using ull = unsigned long long; 15 using pa = pair<int, int>; 16 using ld = long double; 17 ll n, m, k; 18 const int maxn = 1e8 + 1; 19 const double r = 0.57721566490153286060651209; 20 const int mod = 998244353; 21 template <class T> 22 inline T read(T &ret) 23 { 24 int f = 1; 25 ret = 0; 26 char ch = getchar(); 27 while (!isdigit(ch)) 28 { 29 if (ch == '-') 30 f = -1; 31 ch = getchar(); 32 } 33 while (isdigit(ch)) 34 { 35 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 36 ch = getchar(); 37 } 38 ret *= f; 39 return ret; 40 } 41 template <class T> 42 inline void write(T n) 43 { 44 if (n < 0) 45 { 46 putchar('-'); 47 n = -n; 48 } 49 if (n >= 10) 50 { 51 write(n / 10); 52 } 53 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 54 } 55 double a[10010]; 56 void init() 57 { 58 a[0] = 0; 59 for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++) 60 a[i] = a[i - 1] + 1.0 / i; 61 } 62 double h(int n) 63 { 64 if (n <= 10000) 65 return a[n]; 66 return log(n) + r + 1 / (2.0 * n); 67 } 68 double ans[2000100]; 69 void dabiao() 70 { 71 double tmp = 1; 72 for (int i = 2; i < maxn; i++) 73 { 74 tmp += 1.0 / i; 75 if (i % 50 == 0) 76 ans[i / 50] = tmp; 77 } 78 } 79 double solve(int n) 80 { 81 int pre = n / 50; 82 double a = ans[pre]; 83 pre *= 50; 84 ++pre; 85 for (; pre <= n; pre++) 86 a += (ld)1.0 / pre; 87 return a; 88 } 89 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 90 { 91 // init(); 92 dabiao(); 93 int t; 94 read(t); 95 int tot = 0; 96 while (t--) 97 { 98 int n; 99 read(n); 100 printf("Case %d: %.10lf ", ++tot, solve(n)); 101 } 102 return 0; 103 }
View Code
J – Mysterious Bacteria
Description
给出一个n,求一个a^b=n,使得b最大,输出最大的b
Solution
由唯一分解定理可知,要使n可以分解为a^b,b一定为(r1,r2,r3,..rn)。
如果n是负数,特判b是否为奇数,不是奇数b一直除以2


1 //还有对于负数的处理 2 //对于整数,ans=(r1,r2,...rn) 3 //对于负数,先取相反数,然后如果ans为偶数,则一直/2直到不为偶数 4 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 5 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 6 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 7 using namespace std; 8 using ll = long long; 9 using ull = unsigned long long; 10 using pa = pair<int, int>; 11 using ld = long double; 12 ll n, m, k; 13 const ll maxn = 1LL << 31; 14 const int mod = 998244353; 15 template <class T> 16 inline T read(T &ret) 17 { 18 int f = 1; 19 ret = 0; 20 char ch = getchar(); 21 while (!isdigit(ch)) 22 { 23 if (ch == '-') 24 f = -1; 25 ch = getchar(); 26 } 27 while (isdigit(ch)) 28 { 29 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 30 ch = getchar(); 31 } 32 ret *= f; 33 return ret; 34 } 35 template <class T> 36 inline void write(T n) 37 { 38 if (n < 0) 39 { 40 putchar('-'); 41 n = -n; 42 } 43 if (n >= 10) 44 { 45 write(n / 10); 46 } 47 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 48 } 49 int solve(ll n) 50 { 51 int ans = -1; 52 for (ll i = 2; i * i <= n; i++) 53 { 54 int cur = 0; 55 while (n % i == 0) 56 { 57 ++cur; 58 n /= i; 59 } 60 if (cur) 61 { 62 if (ans != -1) 63 ans = __gcd(ans, cur); 64 else 65 ans = cur; 66 } 67 } 68 if (n > 1) 69 ans = 1; 70 return ans; 71 } 72 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 73 { 74 int t; 75 read(t); 76 int tot = 0; 77 while (t--) 78 { 79 ll n; 80 read(n); 81 int f = 0; 82 if (n < 0) 83 { 84 f = 1; 85 n = -n; 86 } 87 int ans = solve(n); 88 if (f) 89 { 90 while (ans % 2 == 0) 91 ans /= 2; 92 } 93 printf("Case %d: %d ", ++tot, ans); 94 } 95 return 0; 96 }
View Code
K – Large Division
Description
给一个大整数n,一个小整数b,判断b能否整除a
Solution
高精度除以低精度,判读最后余数是否为0即可


1 //高精/低精度 2 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 3 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 4 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 5 using namespace std; 6 using ll = long long; 7 using ull = unsigned long long; 8 using pa = pair<int, int>; 9 using ld = long double; 10 ll n, m, k; 11 const ll maxn = 1LL << 31; 12 const int mod = 998244353; 13 template <class T> 14 inline T read(T &ret) 15 { 16 int f = 1; 17 ret = 0; 18 char ch = getchar(); 19 while (!isdigit(ch)) 20 { 21 if (ch == '-') 22 f = -1; 23 ch = getchar(); 24 } 25 while (isdigit(ch)) 26 { 27 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 28 ch = getchar(); 29 } 30 ret *= f; 31 return ret; 32 } 33 template <class T> 34 inline void write(T n) 35 { 36 if (n < 0) 37 { 38 putchar('-'); 39 n = -n; 40 } 41 if (n >= 10) 42 { 43 write(n / 10); 44 } 45 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 46 } 47 vector<int> a; 48 int b; 49 char ss[210]; 50 int solve() 51 { 52 int sz = a.size(); 53 ll t = 0; //注意这里当b为maxInt时,有可能超出int范围,所以应该用ll 54 for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) 55 { 56 t = t * 10 + a[i]; 57 t %= b; 58 } 59 return t == 0; 60 } 61 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 62 { 63 int t; 64 scanf("%d", &t); 65 int tot = 0; 66 char s[2][20] = {"not divisible", "divisible"}; 67 while (t--) 68 { 69 a.clear(); 70 scanf("%s%d", ss, &b); 71 b = abs(b); 72 int len = strlen(ss); 73 if (ss[0] == '-') 74 for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) 75 a.emplace_back(ss[i] - '0'); 76 else 77 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 78 a.emplace_back(ss[i] - '0'); 79 80 int ans = solve(); 81 printf("Case %d: %s ", ++tot, s[ans]); 82 } 83 return 0; 84 }
View Code
Description
依代码行事
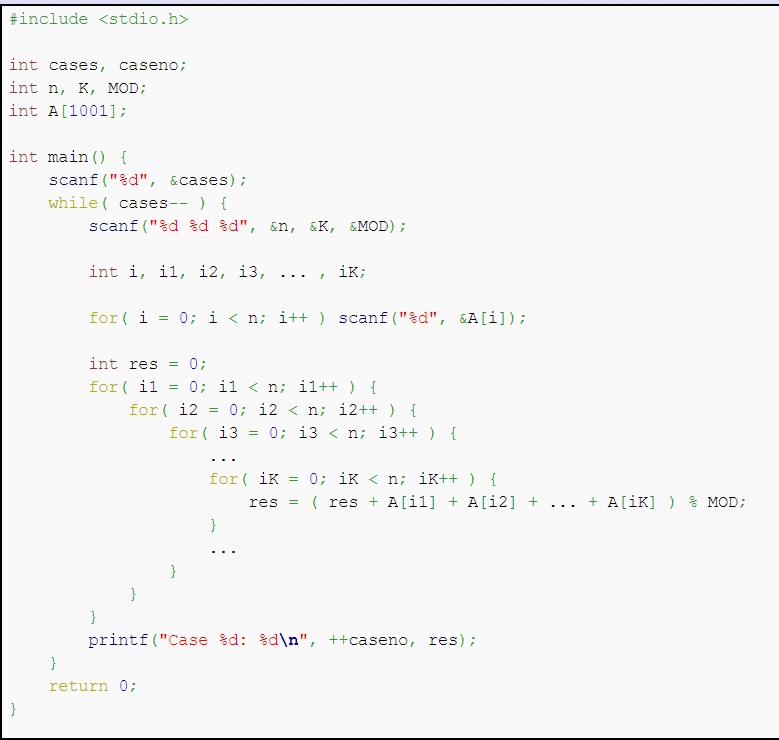
Solution


1 // 找规律发现序列每个数出现次数为n^(k-1) 2 // 快速幂即可 3 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 4 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 5 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 6 using namespace std; 7 using ll = long long; 8 using ull = unsigned long long; 9 using pa = pair<int, int>; 10 using ld = long double; 11 int n, m, k, mod; 12 const ll maxn = 1LL << 31; 13 template <class T> 14 inline T read(T &ret) 15 { 16 int f = 1; 17 ret = 0; 18 char ch = getchar(); 19 while (!isdigit(ch)) 20 { 21 if (ch == '-') 22 f = -1; 23 ch = getchar(); 24 } 25 while (isdigit(ch)) 26 { 27 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 28 ch = getchar(); 29 } 30 ret *= f; 31 return ret; 32 } 33 template <class T> 34 inline void write(T n) 35 { 36 if (n < 0) 37 { 38 putchar('-'); 39 n = -n; 40 } 41 if (n >= 10) 42 { 43 write(n / 10); 44 } 45 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 46 } 47 int qpow(int a, int b) 48 { 49 int ans = 1; 50 while (b) 51 { 52 if (b & 1) 53 ans = ans * a % mod; 54 a = a * a % mod; 55 b >>= 1; 56 } 57 return ans; 58 } 59 int a[1010]; 60 ll solve() 61 { 62 ll ans = 0; 63 ll p = (qpow(n, k - 1) * (k % mod)) % mod; 64 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 65 ans = (ans + p * a[i] % mod) % mod; 66 return ans; 67 } 68 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 69 { 70 int t; 71 read(t); 72 int tot = 0; 73 while (t--) 74 { 75 read(n), read(k), read(mod); 76 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 77 read(a[i]); 78 printf("Case %d: %lld ", ++tot, solve()); 79 } 80 return 0; 81 }
View Code
M – Help Hanzo
Description
给一个区间输出区间内由多少素数
Solution
区间素数筛


1 /* 2 区间素数筛板题 3 注意a为1时需要减去1 4 */ 5 #pragma optimize(3) 6 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 7 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 8 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 9 using namespace std; 10 using ll = long long; 11 using ull = unsigned long long; 12 using pa = pair<int, int>; 13 using ld = long double; 14 int n, m, k, mod; 15 const int maxn = 1e5 + 10; 16 template <class T> 17 inline T read(T &ret) 18 { 19 int f = 1; 20 ret = 0; 21 char ch = getchar(); 22 while (!isdigit(ch)) 23 { 24 if (ch == '-') 25 f = -1; 26 ch = getchar(); 27 } 28 while (isdigit(ch)) 29 { 30 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 31 ch = getchar(); 32 } 33 ret *= f; 34 return ret; 35 } 36 template <class T> 37 inline void write(T n) 38 { 39 if (n < 0) 40 { 41 putchar('-'); 42 n = -n; 43 } 44 if (n >= 10) 45 { 46 write(n / 10); 47 } 48 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 49 } 50 51 ll multiMod(ll a, ll b, ll mod) 52 { 53 ll ret = 0LL; 54 a %= mod; 55 while (b) 56 { 57 if (b & 1LL) 58 ret = (ret + a) % mod, --b; 59 b >>= 1LL; 60 a = (a + a) % mod; 61 } 62 return ret; 63 } 64 65 bool isprime1[maxn], isprime2[maxn]; 66 int solve(ll a, ll b) 67 { 68 for (ll i = 0; i * i <= b; i++) 69 isprime1[i] = 0; 70 for (ll i = 0; i <= b - a; i++) 71 isprime2[i] = 1; 72 for (ll i = 2; i * i <= b; i++) 73 { 74 if (!isprime1[i]) 75 { 76 for (ll j = i + i; j * j <= b; j += i) 77 isprime1[j] = 1; 78 for (ll j = max(2LL, (a + i - 1) / i) * i; j <= b; j += i) 79 isprime2[j - a] = 0; 80 } 81 } 82 int sum = 0; 83 for (int i = 0; i <= b - a; i++) 84 if (isprime2[i]) 85 sum++; 86 if (a == 1) 87 --sum; 88 return sum; 89 } 90 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 91 { 92 int t; 93 read(t); 94 int tot = 0; 95 while (t--) 96 { 97 int a, b; 98 read(a), read(b); 99 printf("Case %d: %d ", ++tot, solve(a, b)); 100 } 101 return 0; 102 }
View Code
N – Trailing Zeroes (III)
Description
给一个整数n,判断n!末尾0有多少个
Solution


1 /* 2 n!末尾0的个数只与5这个素因子有关 3 有公式f(n,p)=f(n/p,p)+n/p,求n!内因子p的个数 4 打表可知出现n个0的情况在4*n+1以后,由此可以将区间确定在一个小范围 5 */ 6 #pragma optimize(3) 7 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 8 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 9 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 10 using namespace std; 11 using ll = long long; 12 using ull = unsigned long long; 13 using pa = pair<int, int>; 14 using ld = long double; 15 int n, m, k, mod; 16 const int maxn = 1e5 + 10; 17 template <class T> 18 inline T read(T &ret) 19 { 20 int f = 1; 21 ret = 0; 22 char ch = getchar(); 23 while (!isdigit(ch)) 24 { 25 if (ch == '-') 26 f = -1; 27 ch = getchar(); 28 } 29 while (isdigit(ch)) 30 { 31 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 32 ch = getchar(); 33 } 34 ret *= f; 35 return ret; 36 } 37 template <class T> 38 inline void write(T n) 39 { 40 if (n < 0) 41 { 42 putchar('-'); 43 n = -n; 44 } 45 if (n >= 10) 46 { 47 write(n / 10); 48 } 49 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 50 } 51 ull f(ull n, int p) 52 { 53 if (n == 0) 54 return 0; 55 return f(n / p, p) + n / p; 56 } 57 ull solve(ull n, int p) 58 { 59 for (ull i = 4 * n + 1;; i++) 60 { 61 if (f(i, p) == n) 62 return i; 63 if (f(i, p) > n) 64 return 0; 65 } 66 } 67 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 68 { 69 int t; 70 read(t); 71 int tot = 0; 72 while (t--) 73 { 74 ull a; 75 read(a); 76 ull ans = solve(a, 5); 77 if (!ans) 78 printf("Case %d: impossible ", ++tot); 79 else 80 printf("Case %d: %llu ", ++tot, ans); 81 } 82 return 0; 83 }
View Code
O – GCD – Extreme (II)
Description
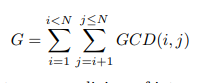
给N,求G
Solution


1 #pragma optimize(3) 2 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 3 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 4 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 5 using namespace std; 6 using ll = long long; 7 using ull = unsigned long long; 8 using pa = pair<int, int>; 9 using ld = long double; 10 int n, m, k, mod; 11 const int maxn = 4e6 + 10; 12 template <class T> 13 inline T read(T &ret) 14 { 15 int f = 1; 16 ret = 0; 17 char ch = getchar(); 18 while (!isdigit(ch)) 19 { 20 if (ch == '-') 21 f = -1; 22 ch = getchar(); 23 } 24 while (isdigit(ch)) 25 { 26 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 27 ch = getchar(); 28 } 29 ret *= f; 30 return ret; 31 } 32 template <class T> 33 inline void write(T n) 34 { 35 if (n < 0) 36 { 37 putchar('-'); 38 n = -n; 39 } 40 if (n >= 10) 41 { 42 write(n / 10); 43 } 44 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 45 } 46 int phi[maxn]; 47 ull r[maxn], a[maxn]; 48 void init() 49 { 50 for (int i = 1; i < maxn; i++) 51 phi[i] = i; 52 for (int i = 2; i < maxn; i++) 53 { 54 if (phi[i] == i) 55 for (int j = i; j < maxn; j += i) 56 phi[j] = phi[j] / i * (i - 1); 57 } 58 for (int i = 1; i < maxn; i++) 59 for (int j = 2 * i; j < maxn; j += i) 60 a[j] += (ull)phi[j / i] * i; 61 for (int i = 2; i < maxn; i++) 62 r[i] = r[i - 1] + a[i]; 63 } 64 inline ull solve(int n) 65 { 66 return r[n]; 67 } 68 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 69 { 70 init(); 71 while (read(n)) 72 { 73 write(solve(n)); 74 putchar(' '); 75 } 76 return 0; 77 }
View Code
P – Code Feat
Description
给出q组同余方程,求出自小的p个解,一个值满足一组方程内的一个即可,保证除数互素
Solution
同余方程组!除数互素!中国剩余定理,gkd! 不对劲儿,冷静思考


1 #pragma optimize(3) 2 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 3 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 4 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 5 using namespace std; 6 using ll = long long; 7 using ull = unsigned long long; 8 using pa = pair<int, int>; 9 using ld = long double; 10 const int maxn = 210; 11 template <class T> 12 inline T read(T &ret) 13 { 14 int f = 1; 15 ret = 0; 16 char ch = getchar(); 17 while (!isdigit(ch)) 18 { 19 if (ch == '-') 20 f = -1; 21 ch = getchar(); 22 } 23 while (isdigit(ch)) 24 { 25 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 26 ch = getchar(); 27 } 28 ret *= f; 29 return ret; 30 } 31 template <class T> 32 inline void write(T n) 33 { 34 if (n < 0) 35 { 36 putchar('-'); 37 n = -n; 38 } 39 if (n >= 10) 40 { 41 write(n / 10); 42 } 43 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 44 } 45 int limit = 10000; 46 unordered_set<int> se[maxn]; 47 int m[maxn], y[maxn][maxn], k[maxn], b[maxn]; 48 vector<int> res; 49 int c, s; 50 ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) //求逆元 51 { 52 if (b == 0) 53 { 54 x = 1, y = 0; 55 return a; 56 } 57 ll ret = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x); 58 y -= (a / b) * x; 59 return ret; 60 } 61 62 ll crt() 63 { 64 ll d, x, y, ret = 0; 65 ll temp; 66 ll M = 1; 67 for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) 68 M *= m[i]; //m是除数 69 for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) 70 { 71 temp = M / m[i]; 72 d = exgcd(m[i], temp, x, y); //求temp在模mi意义下的逆元 73 ret = (ret + y * temp * b[i]) % M; //b是余数 74 } 75 return (ret + M) % M; 76 } 77 void dfs(int dep) 78 { 79 if (dep == c) 80 { 81 res.emplace_back(crt()); 82 return; 83 } 84 for (int j = 0; j < k[dep]; j++) 85 { 86 b[dep] = y[dep][j]; 87 dfs(dep + 1); 88 } 89 } 90 void solveCrt() 91 { 92 dfs(0); 93 ll lcm = 1; 94 sort(res.begin(), res.end()); 95 for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) 96 lcm *= m[i]; 97 for (int i = 0; s; i++) 98 { 99 int sz = res.size(); 100 for (int j = 0; j < sz && s; j++) 101 { 102 ll now = lcm * i + res[j]; 103 if (now > 0) 104 { 105 write(now); 106 puts(""); 107 --s; 108 } 109 } 110 } 111 } 112 void solveEnum(int best) 113 { 114 for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) 115 { 116 if (i == best) 117 continue; 118 se[i].clear(); 119 for (int j = 0; j < k[i]; j++) 120 se[i].insert(y[i][j]); 121 } 122 for (int i = 0; s; i++) 123 for (int j = 0; j < k[best] && s; j++) 124 { 125 ll now = m[best] * i + y[best][j]; 126 if (!now) 127 continue; 128 int f = 1; 129 for (int p = 0; p < c; p++) 130 { 131 if (p != best && !se[p].count(now % m[p])) 132 { 133 f = 0; 134 break; 135 } 136 } 137 if (f) 138 { 139 write(now); 140 puts(""); 141 --s; 142 } 143 } 144 } 145 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 146 { 147 while (read(c) && read(s)) 148 { 149 res.clear(); 150 int best = 0, tot = 1; 151 for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) 152 { 153 read(m[i]), read(k[i]); 154 for (int j = 0; j < k[i]; j++) 155 read(y[i][j]); 156 sort(y[i], y[i] + k[i]); 157 if (m[best] * k[i] < m[i] * k[best]) 158 best = i; 159 tot *= k[i]; 160 } 161 if (tot >= limit) 162 solveEnum(best); 163 else 164 solveCrt(); 165 puts(""); 166 } 167 return 0; 168 }
View Code
Q – Emoogle Grid
Description
给出一个n*m迷宫,k种颜色,里面有p个点不能染色,上下相邻的点不能是相同颜色,在mod 100000007的条件下的染色方案有res种,
m,k,p,res已知,求最小的n
Solution


1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 3 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 4 using namespace std; 5 using ll = long long; 6 using ull = unsigned long long; 7 using pa = pair<int, int>; 8 using ld = long double; 9 const int maxn = 5100; 10 const int mod = 100000007; 11 ll n, k, m, pre, r; 12 template <class T> 13 inline T read(T &ret) 14 { 15 int f = 1; 16 ret = 0; 17 char ch = getchar(); 18 while (!isdigit(ch)) 19 { 20 if (ch == '-') 21 f = -1; 22 ch = getchar(); 23 } 24 while (isdigit(ch)) 25 { 26 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 27 ch = getchar(); 28 } 29 ret *= f; 30 return ret; 31 } 32 template <class T> 33 inline void write(T n) 34 { 35 if (n < 0) 36 { 37 putchar('-'); 38 n = -n; 39 } 40 if (n >= 10) 41 { 42 write(n / 10); 43 } 44 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 45 } 46 ll qpow(ll a, ll b) 47 { 48 ll res = 1; 49 while (b) 50 { 51 if (b & 1) 52 { 53 res = res * a % mod; 54 } 55 a = a * a % mod; 56 b >>= 1; 57 } 58 return res; 59 } 60 struct node 61 { 62 ll x, y; 63 } s[maxn]; 64 bool cmp(node a, node b) 65 { 66 if (a.y == b.y) 67 return a.x < b.x; 68 else 69 return a.y < b.y; 70 } 71 inline void exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) 72 { 73 if (b != 0) 74 { 75 exgcd(b, a % b, y, x); 76 y -= (a / b) * x; 77 } 78 else 79 { 80 x = 1, y = 0; 81 } 82 } 83 84 inline ll inv(ll a) 85 { 86 return qpow(a, mod - 2); 87 } 88 ll BSGS(ll a, ll b) 89 { 90 ll m = (ll)sqrt(mod + 0.5); 91 map<ll, ll> x; 92 x[1] = 0; 93 ll ans = 1; 94 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) 95 { 96 ans = ans * a % mod; 97 if (!x.count(ans)) 98 x[ans] = i; 99 } 100 ll pm = inv(qpow(a, m)); 101 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) 102 { 103 if (x.count(b)) 104 return i * m + x[b]; 105 b = b * pm % mod; 106 } 107 return -1; 108 } 109 ll solve() 110 { 111 ll cur = 1; 112 ll ans = 1; 113 ll k1 = n; //可以为k种选择的格子数目 114 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) 115 { 116 if (s[i].x == 1) 117 k1--; 118 if (s[i].x != r) 119 { 120 if (i + 1 < m && s[i + 1].y == s[i].y) 121 { 122 if (s[i].x + 1 != s[i + 1].x) 123 { 124 k1++; 125 } 126 } 127 else 128 k1++; 129 } 130 } 131 cur = cur * qpow(k, k1) % mod; 132 cur = cur * qpow(k - 1, n * r - k1 - m) % mod; 133 if (cur == pre) 134 return r; 135 k1 = 0; 136 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) 137 { 138 if (s[i].x == r) 139 k1++; 140 } 141 cur = cur * qpow(k, k1) % mod; 142 cur = cur * qpow(k - 1, n - k1) % mod; 143 if (cur == pre) 144 return r + 1; 145 //开始可变全为k-1部分 146 pre *= inv(cur); 147 pre %= mod; 148 k = qpow(k - 1, n); 149 r += BSGS(k, pre); 150 return r + 1; 151 } 152 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 153 { 154 int t; 155 read(t); 156 // scanf("%d", &t); 157 int tot = 0; 158 while (t--) 159 { 160 r = 1; 161 read(n), read(k), read(m), read(pre); 162 // scanf("%lld %lld %lld %lld", &n, &k, &m, &pre); 163 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) 164 { 165 read(s[i].x), read(s[i].y); 166 // scanf("%d%d", &s[i].x, &s[i].y); 167 r = max(s[i].x, r); 168 } 169 sort(s, s + m, cmp); 170 printf("Case %d: %lld ", ++tot, solve()); 171 } 172 return 0; 173 }
View Code
R – 青蛙的约会
Description
同余方程求解最小整数解
Solution
扩展欧几里得


1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 4 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 5 using namespace std; 6 typedef long long ll; 7 const int maxn = 5100; 8 const int mod = 100000007; 9 ll n, k, m, pre, r; 10 void swap(ll &a, ll &b) 11 { 12 ll t = a; 13 a = b; 14 b = t; 15 } 16 ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) 17 { 18 if (!b) 19 { 20 x = 1, y = 0; 21 return a; 22 } 23 ll d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x); 24 y -= (a / b) * x; 25 return d; 26 } 27 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 28 { 29 ll x, y, m, n, l; 30 // read(x), read(y), read(m), read(n), read(l); 31 scanf("%lld %lld %lld %lld %lld", &x, &y, &m, &n, &l); 32 char im[] = "Impossible"; 33 if (m == n) 34 { 35 puts(im); 36 } 37 else 38 { 39 ll a = n - m, b = x - y; 40 ll xa, yl; 41 ll d = exgcd(a, l, xa, yl); 42 if (b % d != 0) 43 { 44 puts(im); 45 } 46 else 47 { 48 ll times = l / d; 49 xa *= (x - y) / d; //最终解 50 xa = (xa % times + times) % times; //最小非负整数解 51 printf("%lld ", xa); 52 } 53 } 54 return 0; 55 }
View Code
S – C Looooops
Description

给出A,B,C,以及其数据范围2^k,求执行多少次
Solution
同余方程求解最小整数解


1 // #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 5 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 6 using namespace std; 7 // using ll = long long; 8 // using ull = unsigned long long; 9 // using pa = pair<int, int>; 10 // using ld = long double; 11 typedef long long ll; 12 const int maxn = 5100; 13 const int mod = 100000007; 14 ll n, k, m, pre, r; 15 // template <class T> 16 // inline T read(T &ret) 17 // { 18 // int f = 1; 19 // ret = 0; 20 // char ch = getchar(); 21 // while (!isdigit(ch)) 22 // { 23 // if (ch == '-') 24 // f = -1; 25 // ch = getchar(); 26 // } 27 // while (isdigit(ch)) 28 // { 29 // ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 30 // ch = getchar(); 31 // } 32 // ret *= f; 33 // return ret; 34 // } 35 // template <class T> 36 // inline void write(T n) 37 // { 38 // if (n < 0) 39 // { 40 // putchar('-'); 41 // n = -n; 42 // } 43 // if (n >= 10) 44 // { 45 // write(n / 10); 46 // } 47 // putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 48 // } 49 ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) 50 { 51 if (!b) 52 { 53 x = 1, y = 0; 54 return a; 55 } 56 ll d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x); 57 y -= (a / b) * x; 58 return d; 59 } 60 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 61 { 62 ll a, b, c, k; 63 while (~scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld", &a, &b, &c, &k) && (a + b + c + k)) 64 { 65 k = 1LL << k; 66 ll t = c; 67 c = b - a; 68 a = t, b = k; 69 ll x, y; 70 ll d = exgcd(a, b, x, y); 71 if (c % d) 72 { 73 puts("FOREVER"); 74 continue; 75 } 76 ll r = c / d; 77 x *= r; 78 ll ra = b / d; 79 x = (x % ra + ra) % ra; 80 printf("%lld ", x); 81 } 82 return 0; 83 }
View Code
T – Death to Binary?
Description
模拟题,实锤了
Solution


1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #define ll long long 3 #define lson l, m, rt << 1 4 #define rson m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1 5 using namespace std; 6 7 char str1[50], str2[50]; 8 char a[50], b[50], c[50]; 9 int solve(char a[]) 10 { 11 int k = 50; 12 while (k >= 0 && a[k] == 0) 13 k--; 14 while (k >= 0) 15 { 16 if (a[k] >= 1) 17 { 18 while (k - 1 >= 0 && (a[k - 1] >= 1 && a[k] >= 1)) 19 { 20 a[k + 1]++, a[k]--, a[k - 1]--; 21 if (a[k] == 0) 22 { 23 k--; 24 break; 25 } 26 else if (a[k - 1] == 0) 27 { 28 k -= 2; 29 break; 30 } 31 } 32 if (k - 1 >= 0 && a[k - 1] == 0) 33 { 34 while (a[k] >= 2) 35 { 36 if (k > 1) 37 a[k] -= 2, a[k + 1]++, a[k - 2]++; 38 else if (k == 1) 39 a[k] -= 2, a[k + 1]++, a[k - 1]++; 40 else 41 { 42 k--; 43 break; 44 } 45 } 46 k--; 47 } 48 else if (k >= 0) 49 k--; 50 } 51 else 52 k--; 53 } 54 k = 0; 55 while (k < 50 && a[k] == 0) 56 k++; 57 if (k == 0) 58 { 59 while (a[0] >= 2) 60 { 61 a[1]++; 62 a[0] -= 2; 63 } 64 } 65 while (k < 50) 66 { 67 if (a[k] >= 1) 68 { 69 while (k + 1 < 50 && (a[k + 1] >= 1 && a[k] >= 1)) 70 { 71 a[k + 2]++, a[k]--, a[k + 1]--; 72 if (a[k] == 0) 73 { 74 k++; 75 break; 76 } 77 else if (a[k + 1] == 0) 78 { 79 k += 2; 80 break; 81 } 82 } 83 if (k + 1 <= 50 && a[k + 1] == 0) 84 { 85 while (a[k] >= 2) 86 { 87 if (k > 1) 88 a[k] -= 2, a[k + 1]++, a[k - 2]++; 89 else if (k == 1) 90 a[k] -= 2, a[k + 1]++, a[k - 1]++; 91 else 92 { 93 k++; 94 break; 95 } 96 } 97 k++; 98 } 99 else if (k + 1 > 50) 100 k++; 101 } 102 else 103 k++; 104 } 105 k = 50; 106 while (k >= 0 && a[k] == 0) 107 k--; 108 return k; 109 } 110 111 void print(int ka, int shu, int num) 112 { 113 if (num == 1) 114 printf(" "); 115 if (num == 2) 116 printf("+ "); 117 if (ka >= 0) 118 { 119 for (int i = 0; i < shu - ka; i++) 120 printf(" "); 121 for (int i = ka; i >= 0; i--) 122 { 123 if (num == 1) 124 printf("%d", a[i]); 125 else if (num == 2) 126 printf("%d", b[i]); 127 } 128 } 129 else 130 { 131 for (int i = 0; i < shu; i++) 132 printf(" "); 133 printf("0"); 134 } 135 printf(" "); 136 } 137 138 void print1(int k, int num) 139 { 140 printf(" "); 141 if (num >= 0) 142 { 143 for (int i = num; i >= 0; i--) 144 { 145 if (k == 1) 146 printf("-"); 147 else 148 printf("%d", c[i]); 149 } 150 } 151 else 152 { 153 if (k == 1) 154 printf("-"); 155 else 156 printf("0"); 157 } 158 printf(" "); 159 if (k == 2) 160 printf(" "); 161 } 162 163 int main() 164 { 165 while (~scanf("%s%s", str1, str2)) 166 { 167 memset(a, 0, sizeof a); 168 memset(b, 0, sizeof b); 169 memset(c, 0, sizeof c); 170 int k1 = strlen(str1), k2 = strlen(str2); 171 for (int i = 0; i < k1; i++) 172 a[i] = str1[k1 - 1 - i] - '0'; 173 for (int i = 0; i < k2; i++) 174 b[i] = str2[k2 - 1 - i] - '0'; 175 int ka = solve(a); 176 int kb = solve(b); 177 for (int i = 50; i >= 0; i--) 178 c[i] = a[i] + b[i]; 179 int kc = solve(c); 180 int num = max(max(ka, kb), kc); 181 print(ka, num, 1); 182 print(kb, num, 2); 183 print1(1, num); 184 print1(2, num); 185 } 186 }
View Code
U – Primes
Description
给出一个数n,判断是否素数
Solution
直接搞


1 // #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #include <cmath> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <iostream> 5 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 6 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 7 using namespace std; 8 // using ll = long long; 9 // using ull = unsigned long long; 10 // using pa = pair<int, int>; 11 // using ld = long double; 12 typedef long long ll; 13 const int maxn = 5100; 14 const int mod = 100000007; 15 ll n, k, m, pre, r; 16 int isprime(int x) 17 { 18 if (x == 1) 19 return 0; 20 if (x == 2) 21 return 0; 22 int m = sqrt(x) + 1; 23 for (int i = 2; i <= m; i++) 24 if (x % i == 0) 25 return 0; 26 return 1; 27 } 28 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 29 { 30 int tot = 1, t; 31 while (scanf("%d", &t) && t > 0) 32 { 33 printf("%d: ", tot++); 34 if (isprime(t)) 35 puts("yes"); 36 else 37 puts("no"); 38 } 39 return 0; 40 }
View Code
V – Maximum GCD
Description
输入一行数据,输出其最大公约数
Solution
注意读入


1 // #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 #include <cmath> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <vector> 7 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 8 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 9 using namespace std; 10 // using ll = long long; 11 // using ull = unsigned long long; 12 // using pa = pair<int, int>; 13 // using ld = long double; 14 typedef long long ll; 15 const int maxn = 5100; 16 const int mod = 100000007; 17 char s[maxn]; 18 int gcd(int a, int b) 19 { 20 return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; 21 } 22 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 23 { 24 // ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 25 // cin.tie(0); 26 // cout.tie(0); 27 int t; 28 cin >> t; 29 getchar(); 30 while (t--) 31 { 32 int ans = 0; 33 gets(s); 34 int cur = 0; 35 int sz = strlen(s); 36 vector<int> aa; 37 aa.clear(); 38 for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) 39 { 40 int sum = 0; 41 while (i < sz && s[i] != ' ') 42 { 43 sum = sum * 10 + s[i] - '0'; 44 i++; 45 } 46 aa.push_back(sum); 47 } 48 49 sz = aa.size(); 50 for (int i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++) 51 for (int j = i + 1; j < sz; j++) 52 ans = max(ans, gcd(aa[i], aa[j])); 53 cout << ans << " "; 54 } 55 return 0; 56 }
View Code
W – Prime Time
Description
输入两个区间端点,判断区间内有多少素数,给出百分比
Solution
数据较小,暴力即可
卡精度,需要加eps


1 /* 2 卡精度真的恶心,记得最后加一个eps 3 */ 4 #pragma optimize(3) 5 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 6 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 7 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 8 using namespace std; 9 using ll = long long; 10 using ull = unsigned long long; 11 using pa = pair<int, int>; 12 using ld = long double; 13 int n, m, k, mod; 14 const int maxn = 1e8 + 1e5; 15 template <class T> 16 inline T read(T &ret) 17 { 18 int f = 1; 19 ret = 0; 20 char ch = getchar(); 21 while (!isdigit(ch)) 22 { 23 if (ch == '-') 24 f = -1; 25 ch = getchar(); 26 } 27 while (isdigit(ch)) 28 { 29 ret = (ret << 1) + (ret << 3) + ch - '0'; 30 ch = getchar(); 31 } 32 ret *= f; 33 return ret; 34 } 35 template <class T> 36 inline void write(T n) 37 { 38 if (n < 0) 39 { 40 putchar('-'); 41 n = -n; 42 } 43 if (n >= 10) 44 { 45 write(n / 10); 46 } 47 putchar(n % 10 + '0'); 48 } 49 bool vis[maxn]; 50 int prime[maxn / 10], pcnt; 51 void init() 52 { 53 for (int i = 2; i <= maxn; i++) 54 { 55 if (!vis[i]) 56 prime[pcnt++] = i; 57 for (int j = 0; j < pcnt && i * prime[j] <= maxn; j++) 58 { 59 vis[i * prime[j]] = 1; 60 if (i % prime[j] == 0) 61 break; 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 inline int isprime(int x) 66 { 67 return !vis[x]; 68 } 69 inline int f(int x) 70 { 71 return x * x + x + 41; 72 } 73 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 74 { 75 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 76 cin.tie(0); 77 cout.tie(0); 78 int a, b; 79 init(); 80 while (cin >> a >> b) 81 { 82 ld mu = b - a + 1; 83 ld deno = 0; 84 for (int i = a; i <= b; i++) 85 deno += isprime(f(i)); 86 ld ans = deno / mu * 100; 87 cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << ans + 1e-5 << " "; 88 } 89 return 0; 90 }
View Code
X – Farey Sequence
Description
欧拉函数前缀和
Solution


1 #pragma optimize(3) 2 // #include <bits/stdc++.h> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <iostream> 6 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 7 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 8 using namespace std; 9 // using ll = long long; 10 // using ull = unsigned long long; 11 // using pa = pair<int, int>; 12 // using ld = long double; 13 typedef long long ll; 14 int n, m, k, mod; 15 const int maxn = 1e6 + 100; 16 ll f[maxn]; 17 int phi[maxn], vis[maxn], prime[maxn], cnt; 18 void init() 19 { 20 phi[1] = 1; 21 int cnt = 0; 22 for (int i = 2; i < maxn; i++) 23 { 24 if (!vis[i]) 25 { 26 prime[cnt++] = i; 27 phi[i] = i - 1; 28 } 29 for (int j = 0; j < cnt && i * prime[j] < maxn; j++) 30 { 31 vis[i * prime[j]] = true; 32 if (i % prime[j] == 0) 33 { 34 phi[i * prime[j]] = phi[i] * prime[j]; 35 break; 36 } 37 else 38 { 39 phi[i * prime[j]] = phi[i] * phi[prime[j]]; // phi[i]*(prime[j]-1); 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 f[2] = 1; 44 for (int i = 3; i < maxn; i++) 45 f[i] = f[i - 1] + phi[i]; 46 } 47 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 48 { 49 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 50 cin.tie(0); 51 cout.tie(0); 52 int a, b; 53 init(); 54 while (cin >> a && a) 55 { 56 cout << f[a] << " "; 57 } 58 return 0; 59 }
View Code
Y – The Super Powers
Description
求2^64-1内至少能表示出两个幂的数,打印出来
Solution
暴力打表,注意边界


1 /* 2 暴力打表 3 */ 4 #pragma optimize(3) 5 // #include <bits/stdc++.h> 6 #include <cmath> 7 #include <cstdio> 8 #include <cstring> 9 #include <iostream> 10 #include <set> 11 #define lson rt << 1, l, mid 12 #define rson rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r 13 using namespace std; 14 // using ll = long long; 15 // using ull = unsigned long long; 16 // using pa = pair<int, int>; 17 // using ld = long double; 18 typedef long long ll; 19 typedef unsigned long long ull; 20 int n, m, k, mod; 21 const int maxn = 1e6 + 100; 22 ll f[maxn]; 23 int phi[maxn], vis[maxn], prime[maxn], cnt; 24 unsigned long long maxx = (1ULL << 64ULL) - 1; 25 set<ull> s; 26 ull qpow(ull a, int b) 27 { 28 ull res = 1; 29 while (b) 30 { 31 if (b & 1) 32 res *= a; 33 a *= a; 34 b >>= 1; 35 } 36 return res; 37 } 38 void init() 39 { 40 phi[1] = 1; 41 int cnt = 0; 42 for (int i = 2; i < maxn; i++) 43 { 44 if (!vis[i]) 45 { 46 prime[cnt++] = i; 47 phi[i] = i - 1; 48 } 49 for (int j = 0; j < cnt && i * prime[j] < maxn; j++) 50 { 51 vis[i * prime[j]] = true; 52 if (i % prime[j] == 0) 53 { 54 phi[i * prime[j]] = phi[i] * prime[j]; 55 break; 56 } 57 else 58 { 59 phi[i * prime[j]] = phi[i] * phi[prime[j]]; // phi[i]*(prime[j]-1); 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 64 s.insert(1); 65 for (ull i = 2; i < (1 << 16); i++) 66 { 67 ull tmp = i * i * i; 68 int j = 4; 69 while (1) 70 { 71 tmp *= i; 72 if (vis[j]) 73 s.insert(tmp); 74 ++j; 75 if (tmp > maxx / i) 76 break; 77 } 78 } 79 } 80 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 81 { 82 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 83 cin.tie(0); 84 cout.tie(0); 85 int a, b; 86 // freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout); 87 init(); 88 for (auto x : s) 89 cout << x << " "; 90 return 0; 91 }
View Code
撒花,数论好难呀